At a glance
Efficient material flow optimization in warehouses can yield substantial reductions in OpEx and moderate reductions in energy consumption and CO₂ emissions.
The case in context
Material flow plays a pivotal role in the efficiency of warehouse operations, impacting the distances covered by employees, powered industrial vehicles (PIV) and goods. Improvement of the material flow can contribute to the reduction of non-value-added activities and increase overall warehouse performance.
A closer look: case details and parameters
This case explores four measures to enhance material flow:
- Optimized points of delivery: For this measure, we compare a centralized inbound area with a decentralized one, where the inbound staging areas are dispersed. For the decentralized option, dock doors near the designated racking storage area for each supplier are assigned to incoming trucks. This reduces internal transportation routes.
- Route optimization: Implementing a warehouse management system (WMS) module for optimized operational material flow creates digital inventory transparency, reducing distances for all operational transportation (putaway, picking, and outbound) through route optimization.
- Tech-supported picking: Introducing technology like pick-by-voice, wrist scanners or handhelds within the picking process improves picking efficiency, leading to increased throughput.
- Optimized storage location of items: Through turn rate and seasonality analysis, the positioning of items in racks can be improved in several ways:
a. Minimize putaway distance for fast-mover items and store them at an ergonomic picking height
b. Optimize the location of fast-mover items within the racking aisles to avoid congestion
c. Place items based on seasonality and forecast
d. Place items frequently picked together next to each other
All these improvements further increase picking productivity and reduce covered distances.
Results
The proposed measures for material flow optimization showcase the following benefits for our reference warehouse:
- Over 35% less transportation time for putaway and outbound thanks to shortened putaway distances. This was achieved with optimized points of delivery for trucks and route optimization via the WMS.
- Over 45% shorter picking distances with route optimizations, tech-supported picking and optimized positioning
- Over 15% lower full-time equivalent (FTE) and PIV requirements through all four measures discussed
- Over 15% lower electricity consumption and CO₂ emissions due to reduction in PIV
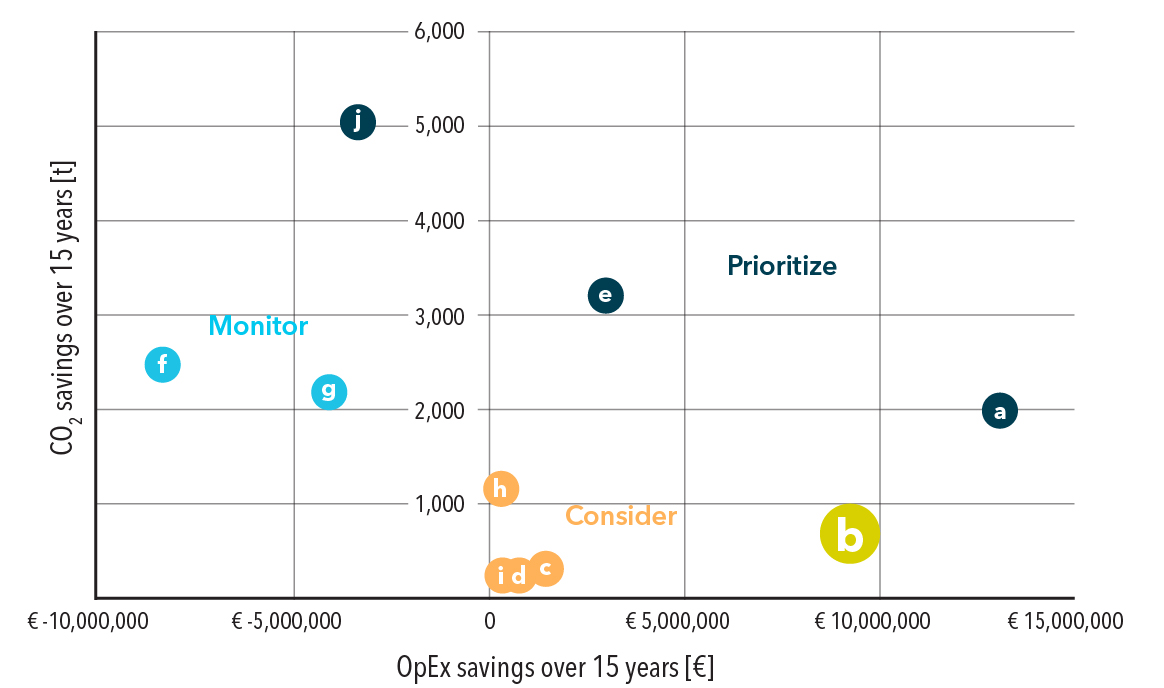
Evaluation: significant OpEx savings and moderate carbon reduction make this lever a first step
Material flow optimization emerges as the second most influential lever for OpEx savings in this case study. Although the impact on CO₂ savings is moderate compared to other cases, the moderate complexity and limited implementation costs (which include internal and external experts and licenses for the relevant WMS module) make these measures accessible. For this reason, material flow optimization is one of the recommended first steps in terms of GHG emissions reduction. When combined with other measures, material flow optimization holds the potential for a significant overall reduction in both CO₂ emissions and OpEx.
Feel free to write us a message